Domestic pollution

We talk very often in the media about external pollution.
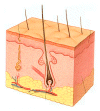
But domestic pollution is a subject that is not addressed and is quite unknown to the public. or each of us stays on average 14 hours a day either at his home or inside the building.
The definition of domestic pollution, you will have understood it, it can no longer be clear: it designates all harmful substances to which one exposes himself or, more broadly, in closed premises (work and leisure places, public spaces, etc.)
Main sources of domestic pollution
1 - Our house equipment and combustion appliances (gas boiler, fireplace, stove, etc.). these devices can produce carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide or ozone
2 - Our daily activities and habits in the home: smoking, use of household products, presence of pets, DIY work, lack of ventilation at the origin of mold development etc.
3 - The materials that were used for the insulation or construction of the building and the components of our furniture and equipment. they may contain or emit formaldehyde, lead, volatile organic compounds (cov,) mineral fibers etc.
Some polluting substances can be found in higher concentrations inside your home than outside.
3 categories of domestic pollutants
1 - On pollutants biological Molds, mites, pets.
2 - On pollutants physical Natural or artificial mineral fibres, gas (e.g. radon,) certain metals (plomb).
3 - On pollutants chemicals : carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds or cov (formaldehyde, benzene, phthalates etc.). nitrogen oxide, particles, pesticides, tobacco smoke, polycholorobiphenyl (pcb,) etc.
Zoom on main domestic pollutants
The main domestic pollutants are tobacco smoke, lead, mineral fibres, nitrogen oxides, particles, allergens, molds, volatile organic compounds (cov) including glycol ethers.
1 - tobacco smoke

It contains up to 4,000 toxic substances. it is carcinogenic, for the smoker but also for its surroundings which is exposed to smoke. It's called passive smoking. In addition to toxic compounds, tobacco releases during its combustion of carbon monoxide and irritating substances. if the smoker remains the most exposed, his entourage also inhales these smokes. the health consequences are numerous: cardiovascular diseases, degradation or destruction of organs constituting the respiratory tract, inflammatory diseases of the intestine, risk of ulcer and other diseases of the digestive system, premature aging of the skin, declining fertility, risk of sudden death is increased in infants, infections of bronchial , nose, throat and ears of children who are more.
2 – Lead

Lead exposure is the cause of saturnism in children and adults. Saturnism is characterized by a set of physical, neurological and/or mental disorders whose severity increases with the importance of exposure.
But where do we find lead in our houses ?
Particularly in the paintings of the former dwellings. Before 1948, the paintings contained lead. it is estimated that approximately 10 million housing units are affected. with the time or occasion of work, paint dust is released.
The presence of lead can also be found in water when it passes through lead pipes. it then takes care of microparticles and it intoxicates those who consume it. lead was very used for inland pipes until the 1950s, and for public pipes until the 1960s. its use then reduced much. It has been banned since 1995. the replacement of existing lead pipes is planned by the end of 2013, for both internal and public network pipelines.
You can also find lead: within the framework of your work (even if the professions exposed are regulated by the labor code: renovation / destruction companies, foundries, metal recovery, etc.).
Once absorbed, lead will be stored by the body. a part is eliminated (mostly by urine), but in much smaller amounts in children than in adults.
If exposure continues, lead concentrations in the organism increase and may have effects over several years, including delay.
3 – Silicous artificial mineral fibres
Thanks to their very good results in terms of acoustic insulation, phonic and heat resistance, these fibers are used in many materials and products. Today we know that these substances are known to be carcinogens for some (asbestos, dairy wool) or highly suspected. The use of asbestos is thus prohibited in france since 1 January 1997. caution is for other types of mineral fibers, in the absence of sufficient data. glass and rock wools were classified by oms as possible carcinogens and, after modifications made by manufacturers, reclassified as "unclassifiable" in 2001.
These fibers can include insulation wools: glass wool, rock wool, dairy wool. natural (asbestos) or artificial, mineral fibres can be hazardous to health if inhaled: as they are often very thin, they penetrate deep into the lungs or migrate to other organs, because the body is unable to eliminate them. They are responsible for lung disease (fibrosis) and respiratory insufficiency, weeping plates and lung and plare cancers (mesothelioma).
Mineral fibres are also very irritating to the skin, eyes and respiratory system.
4 – Nitrogen oxides We find monoxide or nitrogen dioxide in our accommodation. Nitrogen monoxide (no) is produced by high temperature combustions. When it is present in our houses, it can therefore come from industrial activities nearby, motor traffic, gas-operated appliances (kitchen, water heater, gas stove,) wood burning heating appliances (roadway, insert, etc) or gasoline as well as radiators, tobacco smoke. Nitrogen dioxide (no2) when it results from oxidation of nitrogen monoxide.
We find monoxide or nitrogen dioxide in our accommodation. Nitrogen monoxide (no) is produced by high temperature combustions. When it is present in our houses, it can therefore come from industrial activities nearby, motor traffic, gas-operated appliances (kitchen, water heater, gas stove,) wood burning heating appliances (roadway, insert, etc) or gasoline as well as radiators, tobacco smoke. Nitrogen dioxide (no2) when it results from oxidation of nitrogen monoxide.
Health risks: nitrogen oxides can trigger crises in asthmatic people. they can also cause respiratory disorders: irritations, feeling of oppression, cough, discomfort.
An impaired combustion device can also emit carbon monoxide, an odourless and toxic gas that causes nearly 200 deaths each year. it causes headaches and nausea at low doses. as it replaces oxygen in the blood, if exposed to a significant dose of carbon monoxide, there is a risk of loss of knowledge, coma and death by asphyxia.
5 – particles : These are small organic or mineral substances present in suspension in ambient air. they are classified according to their size: particles, fine particles and ultrafine particles (nanoparticles). the smaller they are, the deeper they penetrate the lungs, and the more they can be harmful. they can come from external pollution sources such as road traffic (diesel vehicles without particulate filter) or industrial activities (incinerator, foundry). They may also be related to domestic activities (household, DIY) or individual behaviours (smoking, wood heating). they can be solid or liquid.
These are small organic or mineral substances present in suspension in ambient air. they are classified according to their size: particles, fine particles and ultrafine particles (nanoparticles). the smaller they are, the deeper they penetrate the lungs, and the more they can be harmful. they can come from external pollution sources such as road traffic (diesel vehicles without particulate filter) or industrial activities (incinerator, foundry). They may also be related to domestic activities (household, DIY) or individual behaviours (smoking, wood heating). they can be solid or liquid.
Risks in children: promotes respiratory diseases, especially in babies under 12 months of age, hinders the proper development of lung functions, triggers asthma attacks and may aggravate the disease, is causing coughs, bronchitis, etc.
Risks in adults: fine and ultrafine particles increase mortality from cardiovascular, respiratory or lung cancer.
6 – allergens It is estimated that about 1 in 4 French is allergic. sources are numerous: domestic animals, cockroaches, molds, mites. the effects of exposure to allergens can be accentuated by the irritating power of the following factors: household products: soil washing, dusting for furniture, etc. odour diffusers, scented candles, incense, essential oils, volatile organic compounds (cov) released by furniture, floor coverings, etc. cosmetic products used in sprays, tobacco: this is the worst of the internal pollutants.
It is estimated that about 1 in 4 French is allergic. sources are numerous: domestic animals, cockroaches, molds, mites. the effects of exposure to allergens can be accentuated by the irritating power of the following factors: household products: soil washing, dusting for furniture, etc. odour diffusers, scented candles, incense, essential oils, volatile organic compounds (cov) released by furniture, floor coverings, etc. cosmetic products used in sprays, tobacco: this is the worst of the internal pollutants.
Allergic manifestations can have a significant impact on everyday life: lack of sleep, permanent fatigue, irritability, consequences on professional activities, leisure, school activity, etc.
7 – moulding
It is microscopic mushrooms that develop thanks to the combination heat + humidity. For this reason, they will often be found in bathrooms, kitchens, laundry rooms, cellars, etc.
Molds release spores and/or deodorant substances in ambient air. These spores are inhaled and can be at the origin of: allergic reactions, irritation of the eyes, of the throat, of the nose, of respiratory disorders: cough, whistling breathing, respiratory discomfort, lung infections (especially in fragile people) of skin infections.
8 – Volatile organic compounds (cov) It is chemical substances that are volatile at room temperature. these products can be found for years in homes. We find them in the composition of many products and equipment of our houses. They are very present in our domestic environment: varnish, paints, lacquers, parquet floors, plywood furniture, cleaning and maintenance products, solvents, etc. 80% of homes have a formaldehyde content 5 to 50 times higher than that of the outside.
It is chemical substances that are volatile at room temperature. these products can be found for years in homes. We find them in the composition of many products and equipment of our houses. They are very present in our domestic environment: varnish, paints, lacquers, parquet floors, plywood furniture, cleaning and maintenance products, solvents, etc. 80% of homes have a formaldehyde content 5 to 50 times higher than that of the outside.
Among volatile organic compounds (cov) include benzene, stylene, toluene, trichloroethylene, formaldehyde, glycol ethers. and the list is far from exhaustive!
Their health effects are not yet all well known, but some volatile organic compounds (Cov) are classified as certain or probable carcinogens. observed effects: skin irritation and mucous membranes (eyes, nose, throat,) nausea and headaches, irritations and respiratory system disorders.
9 – household insecticides: pesticides also contaminate the air of housing !
Those responsible are: insecticides, puff, chips, cockroaches, pest control for dogs, cats, wood products.
Possible prevention
1 - tobacco smoke: Quit smoking in the accommodation and you get to the maximum if it is not possible (this will minimize but will not delete them however)
2 - Lead: replacement of pipes if leaded, removal of old paints, do not use kitchen utensils that may contain lead in a professional environment: use adequate protective devices
3 – artificial mineral fibres: avoid drilling, sanding or breaking materials containing asbestos or artificial mineral fibres without being equipped with adequate protections: wearing a mask suitable for the retention of fine elements and gloves. humidify fibre-cement supports to limit emissions of dust when depositing or acting and not treat these materials with high pressure cleaners for example. wastes of products that may contain asbestos should be deposited in a dock that collects this type of waste.
4 – Nitrogen oxides: Very regular aeration of housing to reduce concentrations in indoor pollutants. Consider controlling the operation of domestic combustion appliances, including heating appliances.
5 – particles: Regularly air the housing. for the most sensitive or fragile people, lightly wet linens can be used to make dust and thus trap as much as possible particles without scattering them in the ambient air. vacuum cleaners with a particulate filter will also yield good results.
6 – allergens: reduce exposure to substances you are allergic to.
7 – moulds: Control room temperature and humidity and aerate and ventilate to evacuate excess moisture and condensation.
8 - Cov: Once again, do not hesitate to make a good ventilation and ventilation of the accommodation. on the other hand, additional precautions are used to limit the risks: respect the precautions of use given by manufacturers of maintenance or DIY products, use only the necessary quantities every time, beware of products toxic substances, , corrosive and flammable (pictograms,), do not mix products, do not store products more than necessary, after dry cleaning in a dry cleaner, take care ofaerating clothing before you wear it or store it, limit the use of interior deodorisers. inform you about their possible chemical emissions (les labels indicate levels of pollutant emissions) The European eco-label, or the Blue Angel, are interesting indicators. favor products without emissions or with the lowest emission level, such as the products you will find at home Penntybio.
9 – household insecticides: without hesitation, turn to insecticide products that we market at Penntybio.
In the ideal : preferred biologics products overloaded with solvents, for painting or maintenance products. Today there is a wide range of natural products that can be suitable for all domestic uses of the individual as well as professional: paints, anti-rolls, lasures, lacquers, oils and maintenance products, vitrifiers, waxes, coatings and wall primers, adhesives, mastics, siccatives, decapants. these products not derived from petrochemicals and guaranteed without heavy metals, exist for different supports (minerals, plaster, wood, iron). and it is enough to add colored pigments adapted to get all the desired color shades.
Also turn to the depollutant interior plants. some of them have the capacity to absorb toxic gases or pollutants. these plants capture pollutants and release oxygen in the house. There are many, the best known being cactus, azalea and boston fern.
Special cases of laundry and maintenance products
We have seen it, a large number of products can cause allergies: dish, laundry, glass products, deodorisers, dust, insecticides, weeding, fertilizer, glues, varnish, cleaners, paints, acrylic resins, etc.
Nowadays, the skins are damaged by repeated contacts with laundry still impregnated with detergent and softening, because it was impossible to rinse properly (water saving requires). These detergents do their work, they destroy fat. despite repeated washing, there are always detergent residues that remain in the clothes after the laundry.
The problem is that our skin protects itself from a grease film, destroying it is weakening our skin. Many of us will support this aggression very well because their skin is solid and is not likely to be attacked by the environment.
In several powdered laundry, we find nta, nitrolotriacetic acid, which has carcinogenic effects on rats and laboratory mice.
Unlike some brands, our maintenance products do not contain synthetic tensio-active, enzyme, or coloring, thus helping to minimize any risk of allergy.
You will find detergents on our site. guaranteed without petrochemical but whose efficiency is at least equivalent or better !
Oil derivatives

The vast majority of toiletries made are made with synthetic products, perfumes and petroleum derivatives. this is one of the reasons why a lot of people suffer fromallergies or skin problems such as'irritation, eczema and psoriasis.
There is often the "Paraben"and its derivatives used as a conservative that has a significant allergic potential.
Our skin is not hermetic, it looks like a sponge and absorbs everything. too many people still know that the products they apply to the skin can have consequences on their health.
Some studies have shown that oil-derived ingredients such as sodium lauryl sulfate have carcinogenic effects. before using a product every day and even several times a day, ask yourself the question.
Even if many people are now paying attention to what they eat, it is essential that they become as conscious as soaps, toothpastes, shampoos and anti-sudorifics they buy also have long-term impacts on their health.
Laundry and environment
 That laundry washs our clothes, that's the least thing. but did you know that at the end of the program, every machine rejects in the sewer the dirt of the linen and the laundry ?
That laundry washs our clothes, that's the least thing. but did you know that at the end of the program, every machine rejects in the sewer the dirt of the linen and the laundry ?And that dirty water necessarily ends somewhere. in the best case, these waters are treated in a treatment plant; Most often they join surface waters and their polluting load disrupts aquatic ecosystems.
All residues of laundry are not toxic, but they are dumped in quantities such as they contribute to severe pollution.
Rather disturbing conclusion: the new products that make up the laundry are not completely digested by the purification plants. There is therefore a part of these chemicals that flow into rivers and lakes. but, at the bottom, what are the components that give the laundry its washing power:
- - Tensio-active (or, more simply said, detergents): they are responsible for cleaning. They are therefore indispensable in a laundry.
- - Enzymes: they have the function of getting stains out of blood, cocoa, or egg. they cut the dirt molecules into small pieces, making it easier to dissolve in water.
- - Softeners water attacks the limestone to prevent it from dropping on the linen.
- - The perfume, natural or synthetic.
- - Llaundering agents, which eliminate the spots of coffee, tea or fruit making them invisible. The problem is that they tend to attack also the colors of the clothes.
- - if your clothes look whiter than white, it's the magic effect of optical azuring : they have the power to reflect ultraviolet rays.
- - Anti-repositioning agents : they work hard to prevent dirt, once extracted from the linen, from resting.
- - Anti-disintegration : as their name suggests, they avoid that the coloured garments do not deterate too much on others.
- - finally the revitalizing : thanks to the film it deposits on the fibers, your linen seems soft. innocent at first, all of these agents may not be as white as they look.At the moment, we don't know exactly what these chemicals can pose as a risk to the environment. And when we know what fight it took to get the phosphate ban, there's something to be worried about.







Customer reviews
Nous sommes très satisfaits du service client : mot personnalisé dans le colis, disponibilité du service après-vente... Nous souhaitons à votre société un succès croissant.
Sara
J’ai bien reçu le nouveau diffuseur fonctionnel après essai et je vous remercie pour votre confiance et votre rapidité sur le traitement de mon problème. Ce n’est pas tous les jours que l’on voit un SAV aussi efficace !
Florent
Site très sérieux et personnel vraiment agréable. Envoi rapide. C est parfait !
Ingrid
J'adore. Très grande diversité de produits, les explications sont simples et complètes.Quand aux colis, ils sont extrèmement bien protéger. Un grand merci.
Nadine
Merci pour votre geste que j’apprécie.<br /> Cela fait plaisir de retrouver l’esprit commerçant de proximité chez un vendeur en ligne. Je surveillerai attentivement cette nouvelle livraison.
Philippe
Bonjour. Je souhaite vous remercier pour votre rapidité. Le colis est arrivé en bon état . Les huiles que nous avons commandées embaument la maison. Ce diffuseur est génial.
Christian
Excellents produits. Excellent service.
James T
Très satisfaite. Je recommande cette société sérieuse. bon suivi de la commande.
Sandrine
Produit conforme aux attentes.<br /> <br /> <br /> <br />
Alain
Bravo pour votre sérieux. Colis reçu très vite et produits impeccables. Belles fêtes de fin d'année
Mat
C'est vraiment magnifique et ce cadeau a plu, je commanderais pour Noël.
Martine
j'ai reçu mon colis aujourd'hui, merci c'est très rapide et sérieux.
Nathalie
Bonjour Sophie et Quentin,<br /> Je viens de recevoir ma commande et je tenais à vous remercier pour la rapidité de l'envoi, votre gentil petit mot et le petit présent qui sent bon et donne envie. Bel été à vous deux également
Geneviève
J'ai bien reçu mes articles et je vous remercie pour la livraison rapide et impeccable !
Françoise
Merci à Penn'Ty Bio pour la qualité des produits, la réactivité de l’Équipe et le petit mot attentif qui accompagne les colis. Votre site est précieux !!
Veronique B.
Rien à redire, de la commande à la livraison.
XX
Bon produit mais frais de port un peu cher.
Marie Paule
Ravie de découvrir un site qui présente des produits de qualité avec une vraie démarche éco responsable à des tarifs intéressants.
XX
Produits utilisés depuis très longtemps, toujours la même qualité ! Je recommande, les délais de livraison sont très courts, produits très efficaces.
Laurence
Un grand merci pour cette commande envoyée très rapidement. Je recommanderais votre site
Elise
J'ai passé ma première commande, chez vous il y a trois jours à peine et ce matin, je reçois mon colis.
Sophie
L’esprit commerçant de proximité chez un vendeur en ligne !
Philippe
Toujours impeccable, les produits, les services. Depuis que j'ai changé de facteur, plus de soucis. (Ça n'est arrivé qu'une fois!!!)
XX
Rapide, sérieux, très bien emballé, un sans faute.Merci.
L.H.
sérieux
XX
MOI JE DIS INCROYABLE !!!<br /> Plus que mieux d'une rapidité de dingue ! bravo et le colis impeccable surprotégé.<br /> Que toutes les entreprises prennent exemple sur vous. merci
AURELIE A.
Efficace, livraison rapide.<br /> <br />
H
Françoise
Envoi très rapide et bravo pour votre site de reconnaissance des insectes nuisibles.
Brice
Parfait. Rien à redire. Extrêmement efficace.
Quentin
Cliente depuis plusieurs années. Super service, réactif, cordial. Les produits sont excellents.
Christine
Everything was very nice ! Keep handling your customers likes this!
xxx
Bon site, fiable, rapide et efficace.
Leo L.
Merci. Je tenais à vous faire part de ma grande satisfaction. Je suis enchantée par les produits et par le service. Salutations et bonne continuation,
Odile
Client depuis plus de 10ans. Toujours satisfait du matériel propose. Boutique sérieuse prix compétitifs livraisons et suivis rapide.
XX
je viens de réceptionner ma commande. Tout est ok. Merci pour ces produits respectant l'environnement et l'être vivant.
Anatole
JM
Grande gentillesse et efficacité : que demander de plus ? Merci !
Chantal M.
Bons produits conformes à mes attentes et livraison au top. Je recommande vivement.
Chantal P.
Fiable, et très bons produits , Service après vente efficace et sympathique.
Vilma V.
Pennty bio prends le temps de renseigner et donne de très bons conseils.<br /> Les produits sont emballés soigneusement et la préparation des commandes hyper réactive. Je recommande les yeux fermés !
Mattloumag
Excellent site rapide et efficace. Descriptif intéressant.
XX
Très satisfaite.
Louise
C'est ma première commande chez Penn'Ty Bio, et ce ne sera pas la dernière.<br /> J'étais à la recherche d'un nouveau diffuseur d'HE et, après discussion avec Quentin, mon choix s'est arrêté sur l'Elixia (Direct Nature) qui est d'une efficacité redoutable et d'un silence absolument surprenant.<br /> La livraison s'est faite en 72h en point retrait avec un conditionnement hyper sécurisé.<br /> Lors du déballage, j'ai constaté un léger défaut de finition sur la verrerie.<br /> J'en ai fait part à Quentin par texto avec photos à l'appui.<br /> Il m'a aussitôt recontacté pour me proposer un envoi d'une nouvelle verrerie dès que disponible.<br /> Un professionnalisme et un sens du service exemplaires qui font de cette enseigne une valeur sûre.<br /> Penn'Ty Bio est vraiment la boutique en ligne qu'il vous faut connaître.<br /> Je vous la recommande vivement.
Jean-Yves S.
Très réactifs entre la commande et la livraison. Je suis toujours satisfaite de mes commandes soigneusement emballées !
France L B
clair net précis. merci
jannick
Produits d'excellente qualité, arrivés rapidement, et conformes à leurs descriptions.
Michelle G.
Très bons produits, service rapide et de qualité, rapport qualité/prix intéressant. Je recommande vivement.
Alain
Rapidité de livraison. Très bon produits. Merci
Mélina
merci pour votre professionnalisme. Merci pour les produits envoyés dans de bons délais. Merci pour la qualité de vos produits
Marcelle
Bon produit. Merci Penn'Ty Bio. Un seul passage dilué à 5% et les puces ont disparus. Il en restait deux ou trois qui ont dû se perchés pendant le traitement mais sinon c'est performant.
Axel
Très bien !
XX
Bon rapport qualité-prix. Envoi rapide et sécurisé !
Chrile
Sav rapide et disponible. Au top
Severine
Merci pour cette première commande, envoyée très rapidement, et dans un petit colis, avec frais de port très raisonnables.
Valérie O.
Cela fait plusieurs fois que je commande chez Penn'Ty Bio et je suis toujours satisfaite de la qualité des produits et de la rapidité d'expédition. Je recommande ce site !
Ghyslaine
Client depuis de nombreuses années, je suis satisfait à la fois de la boutique et de pratiquement tous les produits achetés.
Jean-Claude
j'ai reçu mon colis aujourd'hui, merci c'est très rapide et sérieux.
Clara
Jean Claude
très bons produits et service commercial très performant, continuez sur cette voie, merci.
Annick
Personne disponible, de très bon conseil suite à des punaises de lits dans mon habitation, les produits sont efficaces car depuis aucune punaises et la vie à repris son cours ... merci pour tout
Nathalie
Je vous remercie beaucoup de m’avoir fait profiter d’un acheminement par Colissimo alors que rien ne vous y obligeait, sauf votre conscience professionnelle, chose rare de nos jours et qu’il ne faut jamais manquer de souligner.
Cécile
Livraison très rapide et produits bien emballés.
Catherine
Envoi rapide, emballage au top, continuez comme ça... :-)
bruno b.
livraison rapide, produits bien enveloppés avec juste un petit bémol : pour l'imperméabilisant dont le couvercle n'était pas bien fermé.
Alain
Merci pour tout le soin que vous mettez pour une livraison individualisée, chaleureuse et aussi peu impactante que possible sur l'environnement !
Sandra
Très satisfaite par Penn ty bio. En effet, suite à un produit défectueux ( housse matelas) , j'ai aussitôt reçu un bon de retour pour renvoi gratuit en colissimo et ai reçu la nouvelle housse dans les 48 h, avant même le renvoi de la première housse. Merci pour la réactivité et la confiance de cette entreprise.
dominique B.
Parfait !
Mireille
Commande tout à fait conforme et emballée avec grand soin.
Sarah
Je suis cliente depuis de nombreuses années. Toujours satisfaite du site, des produits et de la livraison.
martine O.
Très bien , bon produits, La prochaine commande avec plaisir, livraison très rapide.<br />
Rainer
Emballage au top. Livraison rapide et sans dégâts.
xxx
Envoie soigné et rapide.<br /> Merci pour le petit mot à la main.<br /> Très appréciable.
XX
fidèle cliente de Penn'Ty Bio, je ne me fournis que chez eux.
XX
Un grand merci pour la qualité et la rapidité de votre réponse.
Tony
Service de qualité, suivi rigoureux, et rapidité au rendez-vous. Les produits sont très fidèles à leur description et pour un coût serré. A recommander fortement.
JACKY
Livré hyper vite. Bravo !
Mick
Commande reçu en 2 jours, impeccable. Tous les produits emballés avec le plus grand soin, petit mot personnalisé! Et encore un petit savon bio au parfum délicieux comme cadeau!! Merci Penn'Ty Bio !!
Orchidée
Parfait comme site, commandes faciles à faire et livraison rapide !
Cindy
Je voulais non pas faire une réclamation; mais vous féliciter pour vos produits que j' ai bien reçue, et également pour la rapidité de votre envoi ce qui est plutôt rare dans d'autre site.
Jérôme
Un grand merci pour votre professionnalisme et la qualité de vos produits. Longue vie à votre site.
XX
De très bons conseils, une livraison rapide et des produits de qualité !
Fabienne P.
Boutique sérieuse. Commande arrivée très rapidement. Merci pour votre gentil mot avec la facture.<br /> <br /> <br />
I Defoy
Service très réactif, emballage soigné , livraison rapide. <br /> Rien à redire . Continuez !!
Sophie
Efficacité de la livraison , très rapide . Produits livres en parfait état . Très bien emballés . Merci.
Geneviève
Bon service et bon produits
Odile R
Parfait comme d'habitude
Sylvain
Très bon produit, conforme à la description.
MICHELE P.
trés satisfaite de ma commande,( produit, et livraison,rapide ) MERCI
Danièle M.
Je me permets de vous écrire un petit mot afin de vous dire que votre site est très bien fait.
Tom
J'adore ce site qui fait un vrai travail de sélection de produits que je ne trouve pas ailleurs et sur une large gamme. Je recommande.
Veronique G.
Service de qualité, suivi rigoureux et rapidité au rendez-vous. Mon colis est arrivé vite même avec un paiement par chèque. Les produits sont très fidèles à leur description et pour un coût serré. A recommander fortement.
Vincent
Service rapide et efficace. Et Sympathique ! toujours un petit mot, ça fait la différence. Et c'est français en plus :). Je recommande.
XX
Bonjour, colis bien emballé arrivé sans encombre, démarche écolo bien ancrée et petit mot perso. Merci à l'équipe de Penn'Ty Bio.
Sofi
En cette période d'avant Noël, je craignais que me colis arriverais en retard. 48h après mon achat, c'était dans la boîte aux lettres. Du coup, je suis large pour mettre mon achat sous le sapin. Merci à vous
Art4
J'ai reçu mon colis hier. Merci de vos démarches,
Sam
Merci pour l'expédition de la pièce de verrerie qui a été recu cette fois sans casse. Meilleures salutations et à très bientôt sur votre site pour un prochain achat .
Louane
J'ai enfin reçu le petit colis, hier. Il a mis un mois pour me parvenir, mais vous n'y êtes absolument pour rien, comme je le pensais, il a été mis de côté lors de la grève nationale. Je vous remercie d'avoir fait faire des recherches, j'ai reçu un mot de la poste.
Hervé
Excellent article sur les diffuseurs d'huile essentielles ! grâce à lui j'ai pu faire mon choix basé sur une excellente analyse de votre part !
Laurence
J'apprécie depuis de nombreuses années la qualité de vos produits et le sérieux de votre site. Une petite mésaventure avec un diffuseur me permet de vous féliciter pour la réactivité de votre SAV. Bravo !
Thierry G.
livraison rapide ,prix raisonnable , produits super efficace j'ai vite calmé mes douleurs lombaires ...enfin soulagée . Merci pennty bio
JEANNINE
Mon avis sur penntybio, très bon produit sur ce site pas une gamme monstrueuse mais que du très bon, et pareil pour les livraisons ultra rapides et le excellent sav si besoin. Je recommande vivement. Client depuis 2018 aucun soucis.<br /> <br />
thierry g.
livraison impeccable, produit bien emballé et correspondant au descriptif, excepté pour la surface de diffusion, ma salle principale doit faire 25m2 maximum et ça ne se diffuse pas au-delà.
Pascale
Juste ce petit mail pour vous dire que j'ai bien reçu votre colis et que mon patron est enchanté ! Ca embaume les huiles essentielles dans le bureau et... ça ne fait pas de bruit ! Encore un grand merci pour votre gentillesse et votre souplesse commerciale.
Sonia
C'est la deuxième fois que je commande sur ce site. J'ai découvert qu'il existait des verreries aux dimensions différentes. Mon diffuseur étant ancien, j'ai chercher le modèle le plus adapté et j'ai trouvé! Mon diffuseur fonctionne à nouveau
Christiane D.
Hyper cher :: très déçue du prix par rapport à la quantité de produit acheté. Sur le site internet, les flacons semblent grands, or pour 80 euros je me retrouve avec 4 flacons de petits produits insecticides... trop cher
xxx
Toujours très bien et parfaitement emballé ! Merci<br />
Valérie
Bonjour, je voulais vous féliciter pour la clarté de votre site, la rapidité de la livraison et la qualité de l'emballage.
catherine R.
Tout est parfait : la qualité des produits, la rapidité d'expédition, la qualité du colis. Je suis enchantée et resterai fidèle à ce site.
Dominique
Envoi très rapide, personnalisé et soigné. Merci
XX
Colis bien arrivé. Emballage remarquable. Diffuseur très joli, très efficace et peu bruyant avec de la couleur qui change. Très satisfaite de la commande.
Sabrina
Super, envoi rapide,bien protégé et petit cadeau !
xx
Site intéressant. Je l'ai découvert, en fait. Produits ménager éco-responsable. Bon pour la maison et non agressifs. Merci.
Mydiadao
Produits performants. Très satisfaite de vos services.
XX
Je suis une amie de vos parents et suis toujours très satisfaite de tous vos produits. Ne changez rien et bonne continuation.
Marité D.
Tout était parfait l’envoi la livraison merci beaucoup
XX
Après un souci sur l’article livré, le site a fait preuve d’une excellente communication (simple et efficace par sms) qui m’a permis de me faire livrer un 2nd article par la marque très rapidement. Parfait !
Pierre
Je vous remercie de votre professionnalisme et de votre réactivité.C'est loin d'être toujours le cas lorsque l'on commande sur internet.
Gaëlle
Produits de bonne qualité, naturels et efficaces, expédition rapide et bien emballée, sav très rapide suite à une erreur de ma part,
XX
Excellents services, très serviable
XX
J'ai bien reçu le colis sans aucun problème. Merci pour la rapidité et le sens du service.
Nicolas
Je viens de recevoir la pastille noire aujourd'hui et je vous remercie de votre envoi gratuit (ce qui est rare de nos jours).
Laurence
très bien je recommande.
Sylvie
Parfait! Préparation et expédition de la commande hyper rapides. Emballage très soigné (j'ai acheté un produit fragile). <br /> Je suis très satisfaite!
Elise M.
Très bon site avec de très bons produits et un soin particulier apporté à la préparation de chaque commande... De plus, Sophie et Quentin prennent la peine d'écrire un petit mot de remerciement avec la commande envoyée....c'est peu commun mais très sympa....:-)
STEPHANE P.
Très satisfait de Penn'Ty Bio : choix étendu,prix raisonnables délais de livraison rapides.
xx
Bonjour Monsieur,<br /> Nous nous étions parlés au téléphone il y a quelques années. Bravo pour l'évolution de votre site et vos dossiers instructifs. Vos produits aussi sont très bons. Bonne continuation, bien cordialement.
Marina
Très contente d'avoir découvert ce site internet ! Du conseil jusqu'à l'achat c'est super. J'étais très embêtée après l'apparition de petit insecte chez nous (des anthrenes) et c'est le seule site internet e-boutique qui a pu nous renseigner dessus et enfin indiquer les produits pour les éradiquer sans pour autant nuire à notre santé (mais en respectant les conseils d'utilisation bien sûr). J'ai reçu ma commande rapidement, et avec surprise un petit mot de remerciement personnalisé avec mon nom dessus. Des détails qui au finale font la différence. Un service de qualité rien à dire. Merci !
XX
Produits conformes aux descriptifs. Délai de livraison respecté. Satisfaite du nébuliseur qui est superbe.
VR
Merci pour votre démarche si respectueux de l’humain, des animaux et de l’environnement !
A.F
Très bon produit facile en entretenir, pas cher.
XX
2 commandes à mon actif et jamais déçue. Vous avez gagné une cliente régulière :) Merci pour votre sérieux et le contenu bien rempli de votre site ! c'est super d'avoir une description hyper détaillée de chaque produit.
Magali
Un grand merci pour votre offre et votre professionnalisme. Pour un service en ligne, vous savez vous rendre proche de nous. Bravo et "suerte" !
Pierre M.
Fidèle à votre marque, je tenais par ce mail à vous féliciter vous et votre équipe pour votre longévité. Votre marque est toujours gage de qualité et sérieux.
Céline
Site sérieux. Bons produits.
Magali
Sav très réactif et efficace suite à avarie durant transport. La livraison du produit en remplacement du colis défectueux à été particulièrement rapide. Merci.
Valérie
Noëlle G.
Commande bien reçue. Je suis tout à fait satisfaite. A bientôt.
Tania
Je trouve l'essentiel sur le site à des prix défiants toute concurrence. Continuez comme cela.
XX
Très contente des produits de qualités et une commande reçu très rapidement. Merci
PATRICIA A.
merci de votre disponibilité et amabilité!
Eric
Boutique très sérieuse avec un envoie rapide et des produits super efficaces.
XX
Merci à tanteOdile pour m’avoir fait découvrir votre site. Depuis je suis une cliente assidue. Très satisfaite de la rapidité des envois, de la qualité de vos produits qui sont par ailleurs très bien détaillés par leur composition et leur mode d’emploi. Une amie vous a rejointe également avec la même satisfaction <br /> Continuez.
Marité D.
Commande bien reçue . Je suis très satisfaite Merci pour votre sérieux
LILIANE
BIEN,CONTINUEZ COMME çà.
XX
Livraison très rapide. Notice livrée avec les produits ainsi qu un petit mot très agréable. Produits très efficaces, avec de l huile de coude, on en vient à bout. Le produit concentré nous a permis de tout éliminer. Par précaution, nous avons tout de même utiliser le spray. Dans une pièce, nous avons utilisé le fumigène. Pour les animaux, la mousse semble efficace. Dans quelques jours nous ferons le shampooing et plus tard les pipettes. Mais franchement après avoir utilisé d autres marques qui ne fonctionnaient pas, nous sommes ravies et nous recommandons ces produits. Merci
Virginie C.
Très bon site. Navigation facile. Les commandes sont expédiées rapidement comme annoncé. Aucun problème depuis que je suis cliente. Je recommande Penn'ty bio.<br />
Elvyne
Juste un petit mot pour vous remercier de votre disponibilité et pour vous dire également que je suis très satisfaite des produits que j'ai acheté, ils sont vraiment efficaces.
Barb.
Produit anti puce extrêmement efficace !<br /> Le vendeur a pris une demi-heure de son temps pour m'expliquer absolument tout ce qu'il y avait à savoir sur le produit, de la composition a la mise en œuvre.. Bref au top ! Je recommande donc vivement Penn'ty !
Louis
Bon produits et service !
Rose-Marie
Livraison rapide et petit mot manuscrit joint au colis, vraiment très sympa! Merci et continuez, vous le méritez.
Jean-Pierre
Beaucoup de soins dans la commande reçue. Je recommande!
XX
très bien livraison dans les délais, colis intact, bon produit.
Martine
Site internet complet, beau et facile d'utilisation<br /> Commande complète et correcte.<br /> Commande emballée a la perfection avec du matériel recyclable, compostable<br /> Délai d'envoi respecté même a l'étranger (Pays-Bas)<br /> Mention spécial pour le petit mot personnalisé ++<br /> On sait pourquoi on commande chez Penntybio depuis 10ans :)<br /> Bonne continuation
Jennifer A.
Excellent site d'achat. Très rapide et que de bons produits.
James
Livraison conforme et rapide. Les produits sont emballés dans des emballages recyclables, voire compostables : j'ai beaucoup apprécié. Je recommande ce site.
Patrick
Entièrement satisfaite.
Ch. D.
Très bon site, très sérieux je recommande, produits de qualité et service après vente au top, de plus livraison des plus rapide et produits très bien emballés, tout est parfait
virginie
Site intéressant proposant de bons produits, attractifs et respectant la nature. Le regret c'est le prix de certains articles.<br />
Catherine
Livraison rapide , produits de qualité, je recommande Penn'Ty Bio.
XX
Livraison rapide et très bien emballé et protégé. Très bonne efficacité. <br /> <br />
XX
Les produits achetés sont excellents. Ils répondent parfaitement à ce que je cherchais. Bravo pour votre site
Michel
Je vous remercie pour vos services. C'est très agréable d'être informé de la sorte.
Anthony
Très bien, je recommande cette boutique
Salomé
Louise
Livraison très rapide et produits intacts à l'arrivée grâce à un emballage impeccable.
Etta
Service au top !!!<br /> Colis reçu très rapidement avec un petit mot manuscrit me remerciant de ma commande et de la confiance que je leur ai témoigné <br /> Suffisamment rare pour être signalé <br /> Je vous encourage toutes et tous à les soutenir en passant commande chez eux!!!!<br /> Longue vie à Penn’Ty Bio !!!!<br /> Ils le méritent
Pierre-Steph
Après essais de divers produits, votre insecticide 4J est le seul à être venu à bout des puces ramenées par le chat de la maison. Livraison rapide par chronopost
JEAN MARIE
Commande reçu très correcte, très bon matos, encore merci et bonne continuation.
Dominique et Monique A.
Site de produits naturels et bio très bien fait, agréable et fiable. beaucoup de produits de qualité.
Anne Marie R.
comme toujours excellente réactivité, livraison très rapide et qualité produits TOP. Merci pour votre compétence.
Annick P.
Efficace rapide et à l'écoute. Diversité des produits. Efficacité des produits. Respect des délais de livraison et prise en compte des spécificités client PMR ( ce n'est pas toujours le cas). Site bien fait pour navigation et produits bien mis en valeur. Des promos et des bons de réduction cumulés en fonction des achats. Merci pour votre efficacité rapidité et professionnalisme.
xxx
Un plaisir de recevoir les colis soignés et respectueux de la planète de Penn’Ty Bio. Merci
k.
Livraison rapide et fiable, dès que le chèque a été reçu. Produits de bonne qualité.
Chantal H.
Un diffuseur plus de 80 M², avec huile essentielles eucalyptus, vraiment formidable, on respire mieux et çà sent super bon. Le matin 1 heure, et le soir 2 heures. De jolies couleur, et pour les fêtes une jolie ambiance. Bravo.
PATRICK
Livraison rapide , le tout correspond à mes attentes.
Julie
Site pratique, compétent, prix corrects. Un envoi très rapide, et je dirai "parfait".
Greg
Site sérieux, proposant de bons produits, efficaces en particulier sur les punaises de lit, fléau actuel. Merci car entre les produits et les housses de matelas nous avons réussi à les éradiquer dans deux maisons à deux ans d intervalle. <br /> Bravo aussi pour la livraison la plus écologique possible.
L.C
Pas encore essayé le produit, mais le site est très sérieux. Livraison dans un temps éclair, même si je suis en Belgique. Emballage soigné. On peut faire confiance.
Roberta
Bonjour Sophie & QUENTIN, Merci pour votre petit mot. . . . Ça fait chaud au Cœur de voir qu'il y a encore des Gens Comme VOUS sur cette planète ! Le monde devient de plus en FOU ! ! ! Cordialement.
Dominique T.
Je suis arrivée sur votre site en cherchant un diffuseur que je viens de commander, mais je voudrais vous dire que votre site est très intéressant, bien fait. Vos dossiers sont enrichissants merci
Joelle
Modèle conforme bien emballé délai respecter continuer comme ça parfait.
Carlos
Rapidité de traitement et petit mot avec le colis très appréciable.
XX
Envoi rapide. Rien a redire.
Marie France
J'ai reçu le colis, merci beaucoup de votre promptitude et bonne continuation.
Louise
Au fil de mes commandes (j'en suis à la 5 ou 6ème) décidément, du sérieux et de l'écoute ! chaque fois que j'ai eu un petit problème: contact immédiat, réponse immédiate, et tir rectifié illico ! Dans le top 5 de mes sites internet !
Vincent
Diffuseurs qui sortent vraiment de l'ordinaire, un envoi parfait - merci BCP
Anthony
Colis parfaitement emballé et produits conformes. 1 des produits était très fragile et est arrivé en excellent état, merci :o) Pourquoi achetez à l'étranger alors qu'on a de si belle s entreprises en France? Tarifs identiques ou moins chers que chez Amazon ;o)
Stéphane C.
Vos explications par email ont été très claires et votre diligence dans le traitement de ma commande et de mes demandes est très appréciée.
Henri
Jamais déçue : les produits correspondent à la description et sont livrés rapidement.
Mireille
très satisfaite de ma commande site vraiment sérieux livraison soignée et rapide ,les articles sont conformes a la description,je suis enchantée et recommande vivement
Marie Viviane C.
Bravo et merci : produits de qualité et service TOP... continuez !...
XX
Je tenais à vous remercier pour la commande que je viens de recevoir ce matin. Merci beaucoup et je n'hésiterai pas à recommander sur votre site.
Sandrine
Très satisfaite de ma commande. Emballage soigné et envoi rapide. Merci beaucoup pour votre professionnalisme !
Sophie
Très satisfaite, merci.
Christine
J'ai toujours été satisfaite de mes commandes chez Penn'ty bio. Rapide efficace. Surtout les caractéristiques des produits est claire et complète. et le site contient beaucoup d'informations sur les différentes gammes. Merci pour votre travail et votre activité.
XX
Penn'Ty Bio wonderfully served our family in Switzerland so that we could try the range of Totemsavon products, which are such caring, loving, and consciously manifested creations :)<br /> <br /> By allowing a shipment to Switzerland and elsewhere, I am sure so many more people would be able to benefit from the beautifully selected product portfolio in Penn'Ty Bio and all, together, make a conscious leap by using and demanding a way more purer approach to anything we interact with.<br /> <br /> Thank you so so much Penn'Ty Bio!<br /> <br /> In 8 Love We Heart Trust<br /> <br /> Miguel Ángel
Miguel Ángel
yvette
Très bien ! envoi rapide et conforme à ce qui est annoncé.
Jacqueline S.
Suite à un précédent message notifiant une erreur de produit à la livraison, Penn'Ty bio m'a fait parvenir à titre gracieux le bon produit. Merci
Martine
Dommage, les vendeurs ne savent pas lire les indications inscrites sur les produits qu'ils vendent
XX
Impeccable.
Christine
I had a marvelous experience with ordering and everything ! Thank you for a great service.
XX
Très bon produit juste ce qu'il faut à prix attractifs Envoi rapide.
xx
super emballage écolo...bravo !
Isa
Colis très bien protégé service rapide. Merci. Site très sérieux .
Elios R.
J'ai bien reçu ce jour, en bon état, les 2 diffuseurs galets. Merci aussi pour votre petit mot manuscrit me souhaitant un bel été. Fidèlement,
Annie
J’ai bien reçu mon colis et vous remercie de votre rapidité. Bravo pour le geste écologique et durable. Emballage nickel ! Et mon chat a adoré jouer avec les billes jaunes !
Anouk
Très contente de vos produits.
nathalie G.
Toujours satisfait et pour les prix et pour les produits.
andré a.
livraison rapide, produit conforme.Prix séduisant.
XX
Excellente réactivité !!! Produit en stock, commandé le 23 dec à 8h30, recu le 24 dec à 9h30. On peut guère mieux faire ! Super communication avec le vendeur.
Xavier
C'est extrêmement délicat de votre part d'avoir fait diligence. Je ne manquerai pas de recommander votre site et de souligner votre gentillesse. Encore merci
Michel
Merci pour vos conseils avisés. Et merci pour vos produits de qualité.
Loïc
MERCI au personnel à l’emballage !!! Ma dernière commande était super bien emballée. Elle a résisté aux (épouvantables) chocs subis pendant le transport. Merci
Veronique
Je parlerais de vous a mes amies car vos produits sont vraiment excellents. Bien a vous et tous mes remerciements.
Patricia
Très bon site, du personnel sérieux et la livraison en temps et en heure. Merci
Marine T
Merci à Penn'ty bio d'avoir garder beaucoup de produits de la marque Lerutan et pour le sérieux dans la préparation et l'expédition des colis. Je recommande.
SR
anne-marie B.
Excellentes prestations. Les produits sont formidables, l'emballage aussi. Les délais d'expédition compétitifs. Je recommande vivement Penn'Ty Bio à tous ceux que l'état de la Planète pour les générations futures inquiètent.
XX
Bien reçu. Bravo pour votre extrême rapidité. Merci
Magali
Commande et livraison rapides!<br /> Rien à dire, c'est parfait !
Christine
Très satisfaite des délais, les produits sont bien emballés et le petit mot sympathique est fort agréable!<br />
Sylvana
Site clair, envoi rapide, marchandises bien emballées, et un petit mot charmant!
SM
Je voulais vous remercier +++ pour votre gentillesse et surtout... votre compétence. C'est vraiment de l'excellent travail... j'ai été bluffée :-)<br /> Renseignement téléphonique 10/5 - produit 10/5... encore merci
Maryse
Très bon site. Envoi rapide. Prix moins cher que sur d autres sites. Bravo et bonne continuation.
Camille
Première commande chez Penn'Ty Bio : <br /> - navigation sur le site = 5/5<br /> - préparation du colis = 5/5<br /> - Prix compétitifs = 4/5<br /> - Qualité des produits sélectionnés = 5/5<br /> <br /> Vendeur à recommander.
Gaëlle
Bon choix, bons conseils et service livraison très rapide. J'aime faire mes courses sur ce site.
FDA
Totalement satisfait. Les produits sont super efficaces et tout est très bien suivis. Je recommande vivement ce site.
Stéphane N.
Super !
Yann
Maryse
Je voulais juste vous remercier. J ai reçu mon répulsif " lézards" aujourd'hui, un petit mot super gentil joint à ma commande ça fait plaisir. J espère que ça va fonctionner. Bonne journée à vous et merci.
Cynthia
Bien, la majeure partie des produits sont efficaces. Je connais cette boutique depuis plusieurs années, je recommande ce site.
XX
SATISFAITE
ANNE
colis reçu ce jour, merci pour le flacon offert
Andrée
Les produits ont été très appréciés par la destinataire. <br /> De plus quand on pose une question, on a toujours une réponse, un conseil très rapidement. Merci pour votre réactivité
xxx
Service clientèle très réactif en cas de difficultés. Livraison rapide. Emballage des produits fragiles excellent. Maison sérieuse, je recommande.
Marie
Tout était parfait. Produit, prix, délai.
Marco
J'ai été TRES bien conseillée lors du contact. Produit naturel donc c'est parfait.
Lilla
Je suis vraiment très satisfaite de la prestation de ce fournisseur : délai de livraison très rapide et emballage des produits réalisé avec un maximum de soin. Bravo !!
Eliane
Bons produits. Fonctionnent très bien.
xx
Très satisfaite. Merci.
CM
Parfaitement parfait, je ne me fournis que chez Penn'ty bio depuis qu'ils m'ont débarrassée de punaises de lit.<br />
MARIE CLAUDE G.
Un super magasin en ligne, avec plein de produits disponibles.<br /> L'envoi a été très rapide et soigné, avec une très bonne communication à chaque étape. Bref, une adresse à connaitre et à garder ! Merci !
Pab57
Merci beaucoup pour l'info, c'est rapide chez vous, très appréciable!
Denis
en comparaison d'autres produits employés précédemment, je trouve les vôtres beaucoup plus efficaces et cela sur le court terme ,disparitions des odeurs en combinant les produits suivant vos conseils .
XX
fiable et de bonne qualité pour les services et les produits :)
XX
Après 2 traitements à 3 jours d'intervalle, j'ai réussi à éradiquer toutes les punaises de mon canapé. Produit hyper efficace que je recommande vivement.
Emmanuelle
Toujours aussi "réactif" et efficace<br /> Bravo et merci pour votre professionnalisme.
Annick P.
Comme d'habitude, envoi soigné, produits performants, Merci.
XX
Site de grande qualité !
Rose Anne Marie
Produit de qualité conforme à mes attentes, envoi rapide et soigné, très bien.
Anne
Sophie. A
Commande passée le jeudi soir, colis livré chez mon "commerçant-relais" le samedi matin. Quelle rapidité ! Du vrai professionnalisme !
Emeline
THIERRY
Comme toujours service "au top" réactivité, qualité produits... BRAVO et merci pour la qualité de votre travail
Annick
Vos produits sont de bonnes qualités et les produits très bien emballés
Dominique
Commande bien reçue ! Bien emballée ! ! ! Jolis produits ! Merci !
AYH
Excellent service après vente après un problème d acheminement de colis par la Poste. Une relation client de très grande qualité. <br /> Cordialement,<br /> <br />
PV
Avec les trois lettres BIO dans votre nom, je ne m'attendais pas à découvrir des billes de polystyrène comme matériaux de rembourrage. Il y a certainement plus écolo !
Michel D.
Marie Aline Roux
Je ne connais pas encore tous les produits mais contente de ce que j'ai commandé. En revanche un peu cher quandmême ce qui me limite.
xxx
Bon produit, efficace et laisse une odeur plutôt agréable. Expédition rapide, emballé avec soins. Je recommande
Mary
Les produits sont de bonne qualité. Leur prix est raisonnable. Ils sont livrés rapidement, et en bon état.
XX
excellent.
XX
Livraison efficace et bon contact oral avec mon interlocutrice.
Maussane
Super efficace !!!
xx
Merci beaucoup pour votre rapidité et votre professionnalisme.
Julie
Marie-Noëlle
Explication, commentaire et livraison en un temps record, tout était parfait, même le petit mot de remerciement écrit à la main ! Merci beaucoup
Monique S.
Bravo ! je vous félicite pour votre efficacité ne manquerai pas de vous conseiller. Merci à la prochaine commande
Anthony
Livraison ultra rapide, bien emballée. Produits au top. Parfait !
Caty
Excellent service et livraison rapide. A conseiller pour la santé des animaux (chiens et chats)
MICHEL
J'ai bien reçu le diffuseur et j'en suis très content.
Paul
Merci d'être à l'écoute pour notre terre et vos clients. Encore une fois je suis très satisfaite de ma commande. Et mes compagnons à 4 pattes sont ravis de se protéger en bio. Merci pour votre attention manuscrite en fin du bon de commande..
Raymonde julie L.
Pour ma part j'ai été satisfaite de la réalisation de ma commande et du délai de livraison. Je recommande votre société.
Nelly
Merci pour votre envoi : rapidité, ponctualité, information de suivi du colis etc. Vraiment du bon boulot.
E.G
Super produits accueil plus que parfait gentillesse. Livraison au top merci beaucoup
Christiane
Penn' Ty Bio, c'est ma référence depuis 10 ans au moins. Je ne commande mes produits de toilette et d'entretien que chez eux. Les marques et le service est irréprochable.
GAELLE
Super, livraison rapide, suivi très rigoureux, site de confiance, très sérieux à recommander... Merci pour tout.
Bernard
Très bons produits je les recommande.<br /> Merci à Pennt'ty Bio pour tout, aussi bien pour les commandes et les emballages.<br /> Bravo Pennt'ty Bio.
Bernadette G.
Excellent site. Très à l'écoute. Livraison rapide. Problème avec un piège à guêpes un autre m'a été livré très rapidement. Chapeau et très agréable de tomber sur des gens compétents.<br /> Encore merci.
XX
Infestés de puces de parquet, le produit a agi en moins de 24 heures. Livrés en tout autant de temps. Le seul produit qui ait fonctionné et en plus archi cool pour la nature.
Nicolas
Dimanche soir, invasion de vrillettes du pain. Lundi matin, commande en urgence des produits verts adéquats. Mardi, livraison, traitement et fin de l'invasion.
Jean-Pierre
super contente, j'y trouve facilement les produits dont j'ai besoin et le service est impeccable et gentil !
Hélène S.
Tout va bien. Bonne année 2021.
Bernadette M.
Merci pour votre efficacité et votre gentillesse, commande, livraison, petit mot agréable, tout était parfait !
Sylvie
Livraison rapide et produit conforme à la description. J'approuve à 100% le principe du recyclage des éléments d'expédition. Un produit fabriqué une fois soit avoir plusieurs vie. Bravo pour cette initiative.
Christophe
Livraison en temps record à l'adresse indiquée en France puis départ dans l'océan indien. Reception des produits en quinze jours à l'autre bout du monde : ravie. Je vous laisserai les avis produits une fois utilisés. Le site est très bien fait et très agréable à utiliser. Le petit mot à la main dans le colis humanise la transaction, je l'ai apprécié. Je pense que vos produits sont très utiles et je vous souhaite une belle réussite et sur la durée.
Sylvie D.
Commande reçue assez rapidement. Merci pour votre sérieux.
Émilie
Très satisfait du site livraison rapide.<br />
Michel
Satisfaction totale. Entreprise au top. J'ai téléphoné le lundi matin, malgré que les contacts téléphonique ne sont que l'après midi, une personne très charmante m'a rappelé presque aussitôt pour mes donner les infos que je souhaitais connaître sur ma commande. Bravo. nous sommes mercredi et ma commande est arrivée. Encore bravo continuez comme ça.
Jacques M.
j'ai bien reçu la commande et je vous remercie pour votre efficacité.
Margot
Bons produits, emballage impeccable, livraison super rapide ! Parfait !
XX
produit parfait.
René
Commande reçue rapidement, frais de port raisonnables pour expédition à l'étranger et les produits sélectionnés au top! Merci!
Cédric Adolphe B.
interressante. Beaucoup d'articles référencés. Après pour la lutte contre les punaises de lit, je ne suis pas sure de l'efficacité de certains produits. C'est un vrai fléau ces bestioles.
Francelyne D.
Merci et bravo pour la qualité des produits et du service toujours aussi efficace et performant.
Annick P.
Cliente depuis plusieurs années, j'apprécie toujours ce site. Meilleures salutations.
France
On ne peut pas toujours faire confiance à des sites de ventes sur le web, mais sur Penn'Tio, j' y viens les yeux fermés. Excellente communication avec le service clientèle, un suivi sérieux. Je remercie chaleureusement toute l' équipe.
Sergine T.
Service très professionnel et très rapide. A conseiller fortement.
Didier M.
C’est la première fois que je commande sur ce site et pas déçue livraison rapide de ce produit que l’on ne trouve pas partout. Je recommande
Patrick
J'apprécie les services de Penn'ty bio. Un maximum d'étoiles pour eux.
Ch. D.
Livraison express. Colis toujours aussi bien préparé (cales, flocons, adhésif sur les bouchons qui risquent de couler). Bravo pour votre professionnalisme.
Isabelle
Une utilisation de vos produits a suffit pour nous débarrasser des poissons d'argent. Merci.
Matthieu
bravo pour votre réactivité et la qualité des produits
Annick P.
Merci et surtout, continuez, c'est rare de trouver sur internet une relation aussi personnalisée sur un mode aussi agréable.
Sabine
Parfait ! Envoi rapide et produits de qualité. Merci pour le petit mot. Je suis très satisfaite !<br />
Julieanaïs
Site très sérieux, de très bons produits et la livraison est rapide.<br />
Isabelle
Merci beaucoup pour la rapidité avec laquelle vous m'avez fait parvenir le diffuseur.
Bichette
La livraison est rapide, je n'ai jamais était déçue de ce site, et les produits sont pas chers et de très bonne qualité!
Patricia
Un accueil téléphonique très agréable et de très bons conseils. <br /> Merci à vous.
XX
Franchement, Penn'ty bio, c'est top ♥<br /> Quentin est super réactif, de très bons conseils. Encore merci de votre efficacité.
Hélios ☼♥
Un grand merci pour la qualité et la rapidité de votre réponse.
Simon
Envoi rapide et soigné, produits efficaces et réponse rapide à mes questions. Je recommande.
xx
Commande facile, livraison impeccable et produits fiables. Merci.
Isabelle
Efficacité redoutable. enchanté.
Robert
Super produits, envoi rapide et soigné, conseils et échanges courtois ! Une jolie boutique en ligne pour acheter en toute confiance ! <br />
Patricia
Livraison très rapide. Bravo pour la réactivité
François
livraison tip top tant en temps et en qualité.
XX
Bon produit , envoi rapide.<br /> <br /> <br />
Christine
merci pour le suivi de ma commande et les mails par lesquels vous m'avez tenu informée.
Zoé
Livraison rapide, emballage plus que parfait, le diffuseur NEOLIA est merveilleux pas bruyant, fonctionnement idéal. Merci PENNTYBIO pour votre sérieux, site web à recommander.
CLAUDE
Rapide, sérieux et qualité, produit correspondant à la description, très contente, je recommande votre site et vos produits.
Corinne
Pennty Bio? Einfach genial. Super rapide , bon produits, super service-livraisons. Je vais recommander bientot =)
xxx
Excellente communication, service très rapide (même à l'étranger), emballage parfait ...
Jacques N., Belgique
rien a redire, sauf, le montant des frais de livraison, un peu élevé.
XX
Très satisfaite de ma commande chez Penn'ty bio. Site très détaillé, produit reçu rapidement, message manuscrit très sympathique. Je recommande !
XM
2 commandes à mon actif et jamais déçue. Vous avez gagné une cliente régulière :) Merci pour votre sérieux et le contenu bien rempli de votre site ! c'est super d'avoir une description hyper détaillée de chaque produit.
clara
Rapidité, emballage nickel et écologique, mot de remerciements personnalisé, produits au top....j adore....je suis une nouvelle cliente conquise. Un grand merci...
Hélène P.
accueil téléphonique personnalisé réactif compétent et bienveillant, livraison rapide et conforme. BRAVO merci pour la qualité de votre travail
Annick
ANNE
Client depuis des années Produits de qualités et surtout qualité de service.
XX
Contente de voir que d’autres alternatives naturelles aux produits plus nocifs soient proposés. Entreprise sérieuse dont commandes sont très bien honorées. Merci.
Capzoe
Bonjour <br /> C'était ma première commande sur votre site et j'en suis très satisfaite <br /> Je vous remercie pour votre professionnalisme (site, prise de commande, livraison) ainsi que pour le petit mot qui rend le tout humain. Très belle journée.
CG
Très bien...merci.
Olivier
Commande bien reçue;je suis tout à fait satisfaite;à bientôt
Sonia
Produit performant et raisonnable au niveau prix. Je recommande
XX
Produits facile à utiliser, efficaces et finalement pas plus onéreux, à l'usage que des produits issus de la pétrochimie. Service livraison impeccable. Je recommande +++<br />
XX
Correspond à mes attentes
Henry
Toujours parfait, livraison, emballage, délai et gentil petit mot personnel pour me remercier de ma fidélité.
XX
Commande reçue rapidement, très bien
XX
Tout à fait satisfait de la qualité de la livraison ainsi que du produit commandé.
Régis
Service rapide et efficace. Bons produits
XX
Ma commande s'est déroulée sans aucun problème avec une livraison rapide et soignée. La satisfaction est au rendez-vs ! Continuez ainsi ! Merci et cordialement !
Etoile 07
Très rapide pour la livraison en Belgique et sérieux. Merci<br />
Corinne
Je suis ravi de trouver les produits de qualité et d ‘efficacité incomparable.
Denitza K.
Félicitations pour la qualité de votre site & la valeur de ses informations ! Continuez ainsi ! On a besoin de vous !
Ronald
Après la découverte des punaises de lit dans 2 chambres de notre vieille maison, j'ai trouvé votre site. le dossier m'a été très utile et je suis très contente d'avoir trouvé des produits moins toxiques que ce que proposent les autres sites de vente.<br /> Je vous remercie d'avoir répondu à mon mail car c'est un peu l'affolement quand on découvre chez soi des punaises de lit.
Françoise S.
Quel dommage pour le produit manquant, je vous remercie pour le remboursement.
Didier
Claudine
Envoi rapide et soigné. Emballage ecoresponsable. Je suis ravi d’avoir trouvé des pièces de rechange pour les diffuseurs à huiles essentielles!
Ina L.
Livraison rapide et soignée. J'utilise les produits bio qui sont de très bonnes qualités. Un savon m'a été envoyée par erreur à la place de celui commandé et il m'a été remplacé très rapidement. Bravo pour leur réactivité. Je recommande fortement ce site.
Liliane
J'ai bien reçu ma commande. Com' dab' , rapidité efficacité ...Merci
Sally
Merci pour le geste commercial, et aussi pour les nombreux conseils et l'excellent service client.
Tristan L
Alex
Une boutique en ligne, sympa et très réactive. On apprécie surtout la livraison express. Pas besoin d'être américain pour livrer dans des délais de champion !<br /> <br />
Daniel de Paris
J'ai été très déçue de ne plus trouver mon déboucheur dans mon biocoop habituel, et perplexe en apprenant qu'il était remplacé par un produit à base de soude...c'est comme ça que je vous ai trouvé sur internet.<br /> Alors merci pour le dépannage, pour le mot gentil qui accompagnait mon colis , et bravo pour le calage en amidon de maïs compostable!<br /> Bravo pour votre démarche et à très bientôt.
Cécile D.
Produits livrés rapidement dans un colis non surdimensionné, les produits sont conformes à la description. Je recommande vivement ce site très bien fait !
Hervé
Livraison très rapide et colis emballé soigneusement.Site à recommander.
isabelle d.
Je suis très satisfaite de mon échange avec le service client (personne à l'écoute, de bon conseil). Envoi rapide et soigné, avec un petit mot sympathique de l'équipe, le top!
XX
Site très pratique. Commande aisée. Suivi régulier. Délai de livraison respecté. Colis très soigné. Tout est parfait.
Nicole
Bravo ! je vous félicite pour votre efficacité et ne manquerai pas de vous conseiller.
Nicolas
Je tenais à vous remercier pour votre service de qualité, une livraison toujours rapide, des colis bien emballés - qui évitent fuites et casse, ainsi que pour le petit mot personnalisé joint à chaque commande, c'est toujours très agréable.
Isabelle G
1ère commande. Très satisfaite : Colis expédié très rapidement et bien emballé. Merci pour votre sérieux.
Ghyslaine
Livraison très rapide; Tout était parfaitement emballé. Je referai appel à vous.
JV39
Cliente fidèle depuis plusieurs années, je ne peut que recommander ce site. Tout est parfait. Tous les produits au top, rapidité d’envoi, gentillesse, allez y les yeux fermés vous ne serez jamais déçus.
Marité 06
Une entreprise fiable, efficace, de confiance, chez qui je recommande de faire ses achats.
S.
Jean-Yves
J’ai découvert cette société en faisant une recherche sur Internet pour trouver un insecticide contre les sclérodermes. Je ne peux pas encore juger l’efficacité de chacun des produits par contre je suis très satisfait de la rapidité et de la qualité d’expédition, ainsi que du sérieux de la société. J’ai même reçu un petit échantillon est un mot personnalisé j’ai trouvé ça très sympa! Merci beaucoup et bonne continuation pour votre société que je recommande déjà.
BJ79
Merci beaucoup le colis est arrivé à la poste hier et je te retire aujourd'hui Merci pour votre efficacité et votre rapidité
Ingrid
Très satisfaite du produit.Rapidité et emballage très soigné.SERIEUX.
MARLENE
Prix intéressants. Expédition super rapide à bon prix. Et tout ça de façon agréable !
Alexis M.
Tout est parfait de la commande à la réception. Commander jeudi et reçu samedi. Et très contente de mon achat . Je recommande
Nadege M.
Des produits très efficaces quand on suis dans l'ordre le traitement. Un léger petit bémol sur le spray insecticide, si possible essayer de trouver un spray plus puissant et plus large pour une diffusion optimale dans les coin et recoin inaccessible. Sinon tout est nickel est une excellente qualité de résultat.<br /> PS: Il faut prendre tout les produit pour un traitement efficace en foyer privé (maison).
Florian G.
Content des produits achetés, reçu rapidement et bien emballé. Merci.
XX
Bonjour, j’apprécie depuis longtemps votre travail : la qualité de vos informations et des produits que vous vendez.
Frederic
Les produits achetés sur le site sont de très bonnes qualités, et j'ai été très bien conseillée. Je recommande !
Aurore
Merci pour votre sérieux et la réexpédition ultra rapide d'un achat non conforme (dont vous n'étiez pas responsable).
Marc
Livraison rapide et bien emballé. Petit message manuscrit qui fait plaisir :)
xx
Livraison rapide et avec colis préparé avec soin :)
Florian
Site très réactif livraison rapide le produit Stop tique et puce est parfait sauf le pulvérisateur.
Danielle B.
Hélène
Une grande compétence, Monsieur Dufil est très professionnel et sait soigner ses clients. Quand à la gamme de produits proposés, elle est parfaite et complète.
Alain A.
Livraison rapide. Produits bien emballés.
Bruno
service très efficace à chaque fois que j'ai commandé. aucune mauvaise surprise sur la livraison. je recommande
Agnès
Les produits commandés sont conformes à mes attentes. Quant à l'accueil au téléphone, il est parfait et nous avons toujours trouvé un terrain d'entente. Je fais confiance à Penntybio.<br /> Merci.
XX
Livraison toujours rapide. J'ai expérimentée le service après vente qui à été excellent avec une réparation rapide et sans frais. Je recommande vivement Penn'Ty bio
Nadine
Tout est parfait à chaque fois. L'attention portée va même jusqu'au petit message, c'est agréable. Fidèle aux produits et au site plus que jamais.
xx
Je confirme efficacité sur la préparation et expédition du matériel. un grand merci
Jeremy
Juste un petit mot pour vous remercier du message accompagnant mon colis ! Je croise les doigts pour que les produits marches mais entre-temps, je voulais vous remercier et en profiter pour vous souhaiter à mon tout un joli printemps.
Rose B.G
Parfait.
Philippe
colis dans les temps,emballage parfait,super accueil téléphonique pour renseignement, je recommande ce site.
ROSCO
J'ai découvert ce site en cherchant de la terre de Diatomée. Livraison rapide. Très sérieux. J'ai mis la page dans mes favoris car j'ai repéré d'autres produits.
Isa
Excellent!! Commande passée le lundi, reçue le mercredi!!! Les produits sont en plus de super qualité !
MADELINE
Très bonne adresse où l'on trouve des alternative aux produits chimiques notamment contre les insectes. Le service client est également de très bons conseils.
ck
je vous remercie pour vos services, c'est très agréable d'être informé de la sorte. colis bien reçu Merci pour la rapidité de la livraison
Bernard
Très bons produits efficaces.
XX
Leave a review | See all